Introduction
We will study it all in detail in this unit.
Waves and the Nature of Waves
"A method that transports energy from one point to another without transferring matter is called a wave".
Formation of waves
Disturbance of medium cause of formation of wave-like, we can produce waves by using a rope, slinky spring, and water waves in ripple tanks. Let us discuss them in detail.
Wave Motion by using a Rope
We can produce waves on a rope by attaching one end to a wall and continuously moving the other end up and down, as shown in the figure:
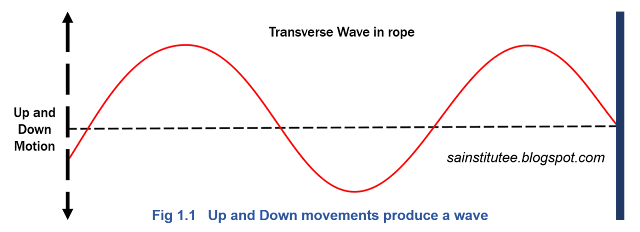
These up-and-down movements produce oscillations or vibrations. We can observe that the generated rope waves travel towards the wall, whereas the rope itself moves only up and down. The rope is the medium through which the waves travel or propagate.
Waves in a Slinky Spring

%20A%20downward%20pulse.%20(c)%20When%20the%20end%20of%20the%20Slinky%20is%20moved%20up%20and%20down%20continuously,%20a%20transverse%20wave%20is%20produced.png)
Now moving the free end of the attached wall slinky spring continuously back and forth as horizontally shown in fig 1.4.

Water wave in (Ripple Tank)
"A ripple tank is a shallow glass tank of water used to demonstrate the basic properties of waves".
It is a particular type of wave tank. The ripple tank is usually illuminated from above so that the light shines through the water to visualize the wave being produced.
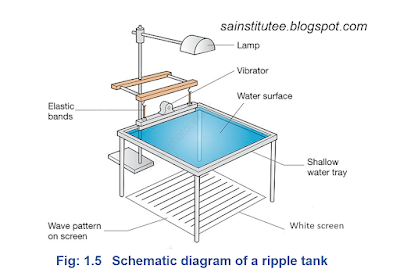
In the laboratory, we can produce water waves with the ripple tank. In the ripple tank, a small vibrator moves up and down the water surface, resulting in the water particles at the surface that are in contact with the dipper being made to move up and down.
This up and down motion soon spread to other parts of the water surface in the tank in the form of ripples; fig. 1.5. Here the water is the medium through which the ripples travel or propagate.
Types of Wave Motion
Transverse Wave
The slinky illustrates the transverse wave in Fig. 1.6. Move the free end of the slinky up and down repeatedly.


Definition: "Transverse waves are waves that travel in a direction perpendicular to the direction of wave motion".
Transverse wave motion can also be observed on the surface of the water in a pond or a ripple tank, as vibrations in a guitar string. Another essential type of transverse wave is electromagnetic waves, e.g., light waves. microwaves, radio waves.
Amplitude
Definition: "Amplitude is the maximum displacement moved by a point on a vibrating body from the rest or mean position".
It is the height of a crest or depth of a trough measured from the rest position as shown in fig 1.8. Its SI unit is meter (m).
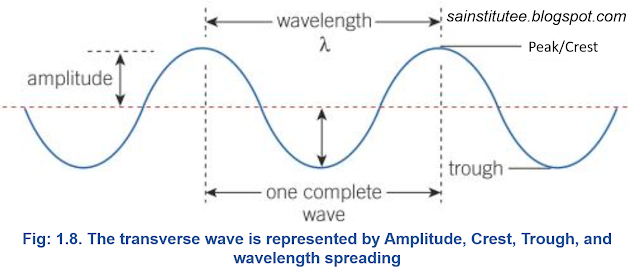
Crest
Trough
Longitudinal Wave
The slinky illustrates the longitudinal wave in Fig. 1.9. Move the free end of the slinky forward and backward (i.e. push and pull) to expand and compress the slinky repeatedly.

These forwards and backward movements of the coils produce oscillations. Have you noticed that when coils move forwards and backward, the direction of the wave motion is parallel to the direction of oscillation? We call this type of wave a longitudinal wave Longitudinal waves can be defined as:
Compression
Rarefaction
Definition: "Rarefaction, in the longitudinal waves, is a region where turns of the coil or particles are further apart than average".








0 Comments